Like a compass in uncharted waters, your parenting journey often leads to countless questions and uncertainties. You'll find yourself wondering about everything from your baby's first solid foods to managing those inevitable toddler meltdowns. As you navigate through each developmental stage, you're bound to face common challenges that every parent encounters, yet each situation feels uniquely personal to your family. Whether you're puzzling over sleep schedules or seeking ways to nurture independence, you're not alone in searching for reliable answers. Let's explore these essential parenting questions together and discover practical solutions that'll help you raise confident, well-adjusted children.
Key Takeaways
- Sleep challenges typically resolve by 4-6 months, with consistent routines and proper room temperature between 68-72°F supporting healthy sleep patterns.
- Solid foods should be introduced around 6 months, starting with iron-fortified cereals and gradually adding pureed fruits and vegetables.
- Toddler tantrums are normal developmental behaviors requiring consistent, calm responses and acknowledgment of emotions rather than punishment.
- Children need 10-15 exposures to new foods before acceptance, making gradual introduction alongside familiar foods an effective strategy.
- Age-appropriate responsibilities build independence, starting with simple tasks at ages 3-5 and progressing to complex duties by ages 10-13.
When Should Babies Sleep Through Night
Most babies develop the ability to sleep through the night between 4-6 months of age, though individual timelines can vary considerably. During this period, your baby's circadian rhythm matures, and they can physiologically handle longer stretches without feeding. You'll notice they can maintain their blood sugar levels and go 6-8 hours without needing nourishment.
Creating a consistent nighttime routine greatly impacts when your baby will sleep through the night. Research shows that predictable bedtime activities, like bathing, reading, or gentle massage, signal to your baby that it's time to wind down.
The sleep environment also plays an essential role – maintain a dark room temperature between 68-72°F, use white noise if helpful, and make certain your baby's sleeping space meets current safety guidelines.
Don't feel discouraged if your baby takes longer to reach this milestone. Some babies might sleep through by 3 months, while others may take up to 12 months.
Medical conditions, growth spurts, and developmental leaps can temporarily disrupt sleep patterns. If you're concerned about your baby's sleep progression, consult your pediatrician for personalized guidance.
Best First Foods for Babies
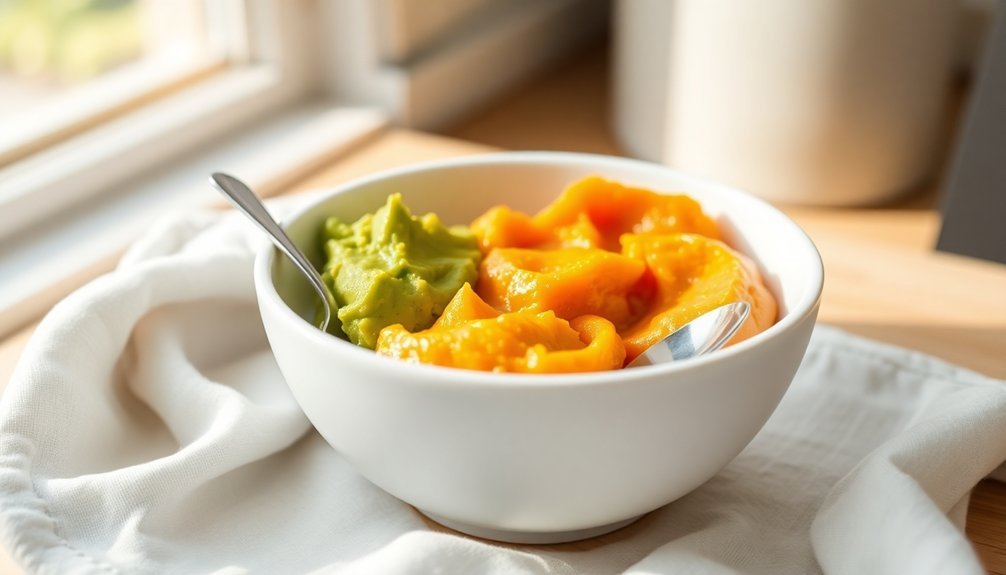

When introducing solid foods to your baby around 6 months of age, iron-fortified single-grain cereals and pureed vegetables provide vital nutrients for development.
Whether you choose traditional nutritious purees or baby led weaning, it's important to focus on iron rich foods like pureed meat, lentils, and fortified cereals. You'll want to establish clear meal timing strategies, starting with one feeding per day and gradually increasing frequency.
Consider these evidence-based first food combinations:
- Sweet potato + breast milk/formula (perfect texture progression)
- Avocado + banana (healthy fats and easy to grip)
- Iron-fortified oatmeal + pureed pears (combines nutrition with natural sweetness)
When exploring fruit and vegetable options, it's important to follow the latest guidelines for allergy introduction. Start with single ingredients, waiting 3-4 days between new foods to monitor reactions.
As your baby develops self feeding skills, incorporate healthy snack ideas like soft-cooked vegetable strips or mashed beans. Research shows that exposing babies to varied textures and flavors during this period can help establish lifelong healthy eating patterns.
Managing Toddler Tantrums

As babies grow into toddlers, feeding challenges often give way to a new parenting test: managing emotional outbursts. You're not alone in facing these challenging moments – understanding toddler triggers can help you navigate them more effectively.
Research shows that tantrums often stem from your child's developing emotional regulation skills. When you identify common triggers like hunger, fatigue, or overstimulation, you'll be better equipped to prevent meltdowns before they start. Maintaining routine consistency helps create a predictable environment that reduces anxiety and outbursts.
Effective communication and positive reinforcement are your allies. When tantrums occur, use simple language to acknowledge your child's feelings while maintaining parental patience. You can say, "I see you're angry" while staying calm yourself.
Environment adjustments, like creating a quiet corner, give your toddler space to process emotions. Distraction strategies work well for minor upsets – redirect attention to a favorite toy or activity.
For major meltdowns, focus on understanding emotions and staying present. Remember, your consistent, calm response helps your toddler develop their own emotional regulation skills over time.
Potty Training Tips That Work
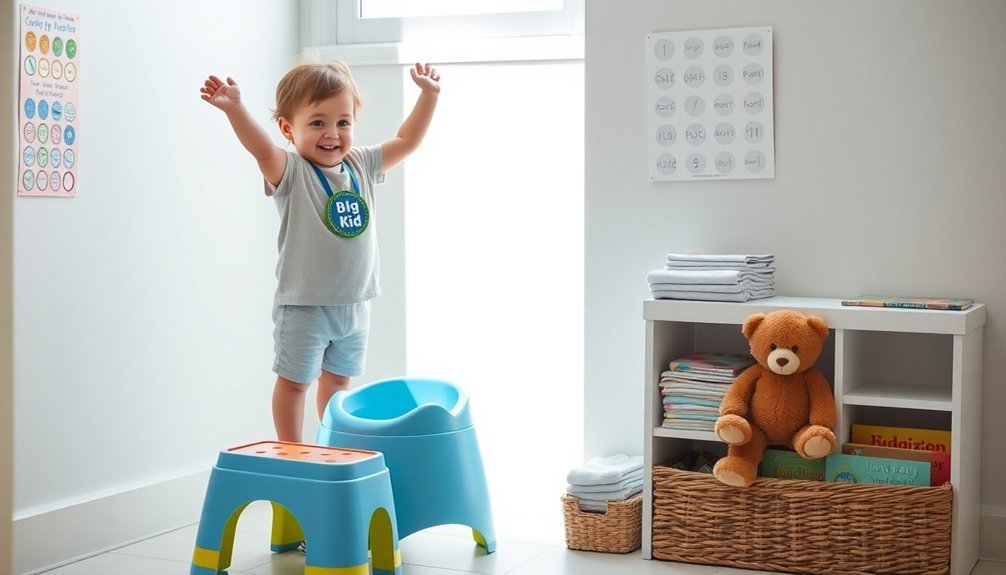

Learning to identify signs of potty training readiness, such as staying dry for longer periods and showing interest in the bathroom, will help you determine the best time to begin training your toddler, typically between ages 18 months and 3 years.
Research shows that using positive reinforcement through a consistent reward system, whether stickers, small treats, or verbal praise, greatly increases successful bathroom visits and motivates children to maintain this new behavior.
Following evidence-based practices, you'll want to establish clear routines and celebrations for potty success while remaining patient with inevitable setbacks, as studies indicate most children achieve complete daytime control within 3-6 months of dedicated training.
When to Start Training
Most children show readiness for potty training between 18 months and 3 years old, though research indicates the average age falls around 27 months.
The key is recognizing your child's potty readiness signs rather than focusing solely on age. You'll want to look for physical, cognitive, and emotional indicators that suggest your child is prepared for this developmental milestone.
Watch for these essential readiness signs before implementing training techniques:
- Physical Control: Your child stays dry for at least two hours during the day and wakes up dry after naps, indicating developed bladder control.
- Communication Skills: They can express basic needs and understand simple instructions about using the bathroom.
- Motor Development: They can walk steadily to the bathroom and pull pants up and down independently.
Don't feel pressured to start too early, as premature training can lead to frustration and setbacks.
Research shows that children who begin training before showing readiness signs often take longer to master toileting skills.
You'll find more success by waiting until your child demonstrates these capabilities, typically resulting in a smoother shift from diapers to independent toileting.
Effective Rewards System
Reward systems play an essential role in successful potty training, with research showing that positive reinforcement greatly increases a child's motivation and progress. When implementing reward charts and incentive programs, it's vital to establish clear, achievable goals that your child can understand and work toward.
Start with frequent rewards for small successes, such as sitting on the potty or telling you when they need to go. You'll find that behavior tracking helps identify patterns and progress, allowing you to adjust your praise strategies accordingly.
As your child masters basic skills, gradually increase the challenge level and space out rewards to build intrinsic motivation. Consider using a combination of tangible rewards (like stickers or small toys) and social reinforcement (enthusiastic praise and celebrations).
Studies show that children respond best to immediate rewards during initial training, but you'll want to decrease reward frequency as they become more consistent. Remember that every child is different – some may respond better to certain types of rewards than others.
The key is to maintain consistency in your approach while being flexible enough to modify your reward system based on your child's unique responses and developmental progress.
Dealing With Picky Eaters
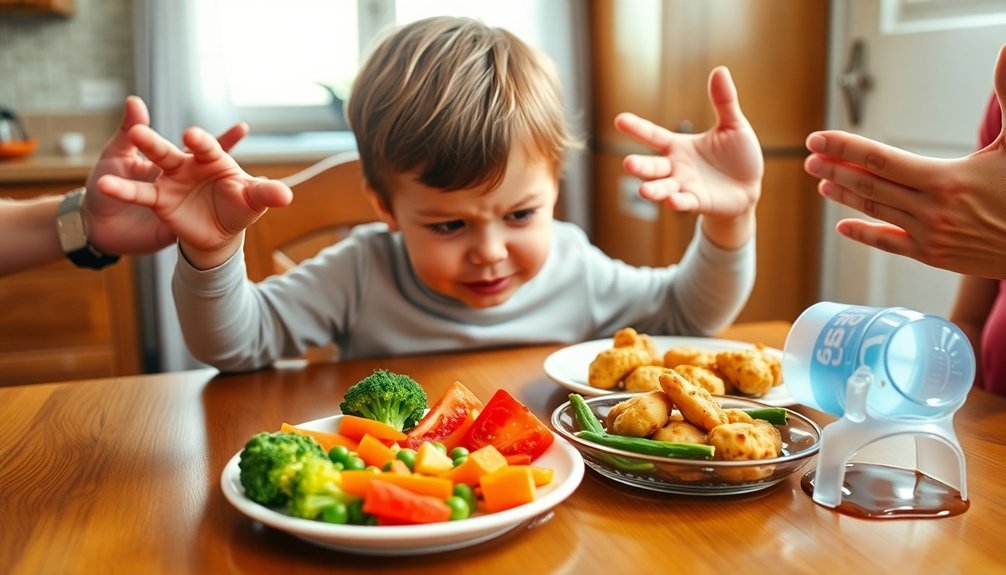

When your child refuses to eat certain foods, it's crucial to implement research-backed mealtime strategies that reduce power struggles and create a positive eating environment.
You'll find success by establishing consistent meal schedules, offering new foods alongside familiar ones, and avoiding the common pitfall of becoming a "short-order cook" who prepares separate meals.
Research shows that gradually expanding your child's food comfort zone through repeated exposure and positive role modeling leads to improved eating habits over time.
Simple Mealtime Strategy Tips
Parents of picky eaters face daily mealtime battles that can turn the dinner table into a zone of stress and frustration.
Research shows that implementing consistent mealtime strategies can transform these challenging situations into positive family experiences. Through mindful meal planning and collaborative family cooking, you'll create an environment that encourages healthy eating habits.
Consider these evidence-based approaches that child development experts recommend:
- Establish a predictable routine by serving meals at the same time each day, which studies show reduces anxiety and increases children's willingness to try new foods.
- Create a "learning plate" alongside the main meal where your child can explore new foods without pressure to eat them – research indicates this reduces food resistance.
- Involve your child in meal planning and preparation, as studies demonstrate that children are 80% more likely to try foods they've helped prepare.
Remember that changing eating behaviors takes time and consistency.
By maintaining a calm, positive atmosphere and avoiding food battles, you're building a foundation for lifetime healthy eating habits.
Research indicates that children may need up to 15-20 exposures to a new food before accepting it.
Expand Food Comfort Zones
How can families help children venture beyond their limited food preferences? Research shows that expanding a child's flavor preferences requires patience, consistency, and strategic exposure to new foods. Studies indicate that children may need 10-15 exposures to a new food before accepting it, making food exploration a gradual process.
You'll find success by incorporating cooking together into your weekly routine. When children participate in meal preparation, they're more likely to try their culinary creations. During family meals, model positive eating behaviors and avoid pressure tactics, as forcing foods can create negative associations.
Transform mealtime adventures into opportunities for food education by discussing ingredients' origins, colors, and textures. Introduce taste diversity through creative recipes that combine familiar foods with new elements. For palate development, offer healthy snacks featuring various flavors and textures throughout the day.
Start small by presenting new foods alongside favorites, and celebrate small victories in food acceptance. Consider implementing a "one-bite" rule without requiring children to finish unwanted foods.
Remember that developing varied eating habits is a journey that strengthens both nutrition and family bonds.
Safe Screen Time Limits

Setting appropriate screen time limits has become increasingly critical as digital devices permeate every aspect of children's lives. The American Academy of Pediatrics has established clear screen time guidelines that you'll want to follow to protect your child's development while allowing beneficial digital media exposure.
Research shows that excessive screen time can impact sleep, physical activity, and social development. You're not alone in struggling to find the right balance – studies indicate that 85% of parents worry about their children's screen time.
To implement healthy boundaries, follow these evidence-based recommendations:
- For children 18-24 months: Allow only video chatting, and always with parent participation.
- For ages 2-5: Limit high-quality programming to 1 hour per day, always co-viewing with your child.
- For ages 6 and older: Create consistent limits, ensuring screens don't interfere with sleep, physical activity, or other essential behaviors.
Remember to model healthy digital media habits yourself.
You can make screen time more meaningful by engaging with your child about the content they're consuming and creating tech-free zones during meals and before bedtime.
Teaching Kids About Money

Growing up financially literate starts with early exposure to money concepts, with research showing that children begin forming money habits as young as age 7. You'll want to integrate money conversations into daily life, using real-world situations to teach budgeting skills and smart shopping decisions.
Start with basic allowance discussions, helping your child divide earnings into spending, saving, and charitable giving categories. As your child develops, introduce more complex financial literacy concepts. You can explore different income sources, from household chores to small entrepreneurial ventures like lemonade stands.
Guide them in setting financial goals, whether it's saving for a toy or contributing to their college fund. Teaching investment basics can start simply with a piggy bank, progressing to a savings account as they grasp the value of money.
Make money management hands-on by involving kids in grocery shopping, comparing prices, and making spending choices. Encourage a healthy relationship with money by modeling debt awareness and responsible financial decisions.
Setting Age-Appropriate Boundaries

Just as children need guidance with money management, they require clear boundaries to develop healthy independence and self-regulation skills. Research shows that effective boundary setting evolves with your child's developmental stages, promoting both security and growth.
Understanding age-appropriate limits helps you create a framework that's neither too restrictive nor too permissive.
When establishing age limits and boundaries, focus on these evidence-based principles:
- Match restrictions to developmental capabilities – toddlers need physical boundaries for safety, while teens require digital and social boundaries that respect their growing autonomy.
- Maintain consistency in your approach – research indicates that children feel more secure and show better behavioral outcomes when boundaries remain steady and predictable.
- Adjust boundaries progressively – as your child demonstrates responsibility and good judgment, gradually expand their freedoms while maintaining clear expectations.
Remember that boundary setting isn't about control; it's about teaching life skills.
Studies show that children who grow up with appropriate limits develop stronger decision-making abilities and healthier relationships. You'll know you're on the right track when your child begins to internalize these boundaries and demonstrate self-discipline.
Choosing the Right School

While academic achievement matters greatly, research shows that finding the right school environment encompasses far more than test scores and rankings. Your child's educational success depends on carefully evaluating multiple factors that align with your family's values and your child's needs.
| Essential Criteria | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Learning Environment | Educational philosophy alignment, class size, curriculum offerings |
| Support Systems | Special education resources, student support services, teacher qualifications |
| Community Aspects | Diversity and inclusion, parental involvement, community engagement |
| Practical Factors | Proximity to home, safety policies, after school programs |
Start by examining each school's educational philosophy to guarantee it matches your child's learning style. Consider class sizes, as research indicates smaller classes often lead to better outcomes. Evaluate the school's technology integration and extracurricular opportunities, which contribute to well-rounded development.
Don't overlook communication policies and feedback mechanisms between teachers and parents. Review conversion programs for new students and assess the school culture through visits. Examine special education resources if needed, and investigate the school's reputation within the community. Remember that the best choice balances academic excellence with a supportive, inclusive environment that nurtures your child's growth.
Handling Sibling Rivalry

Sibling conflicts can shake even the most harmonious household, but research shows they serve essential developmental purposes. When managed effectively, these interactions become valuable opportunities for teaching conflict resolution and fostering sibling bonding.
Studies indicate that children who learn to navigate disagreements with siblings often develop stronger emotional intelligence and social skills.
To promote healthy sibling relationships while minimizing destructive conflicts, you'll want to implement these research-backed strategies:
- Establish clear family rules about acceptable behavior, ensuring each child understands that physical aggression or emotional manipulation won't be tolerated.
- Create designated "alone time" for each child with parents, reducing competition for attention and strengthening individual relationships.
- Teach specific problem-solving phrases and techniques, like "I feel…" statements and taking turns, which children can use during disagreements.
Remember that your role isn't to eliminate all conflicts but to guide your children through them constructively.
When you consistently model fair conflict resolution strategies, you're helping your children develop crucial life skills. Research shows that siblings who learn these skills early often maintain stronger relationships throughout adulthood.
When to Start Solid Foods

Around the 6-month mark, your baby typically develops the physical and developmental readiness for solid foods. You'll notice key signs: they can sit with support, show interest in your food, and have lost the tongue-thrust reflex that pushes food out of their mouth.
Start with iron-fortified single-grain cereals mixed with breast milk or formula, maintaining a thin, smooth food texture. Progress gradually to pureed fruits and vegetables, introducing one new food every 3-4 days to monitor for allergic reactions. This careful approach supports proper allergy awareness and helps you identify any sensitivities early.
Watch for signs that your baby's ready for each feeding: they should open their mouth enthusiastically and lean forward when food's offered. If they turn away or seem uninterested, don't force it.
You'll want to maintain breast milk or formula as their primary nutrition source throughout the first year.
Many parents join baby-led weaning groups for support and guidance. Remember that every baby develops at their own pace, so consult your pediatrician before starting solids, especially if there's a family history of food allergies.
Managing Homework Struggles

Your child's homework battles can signal deeper learning challenges or time management issues that need addressing. Research shows that establishing consistent homework organization and a dedicated study environment greatly improves academic performance and reduces family stress.
To effectively manage homework struggles, implement these evidence-based strategies:
- Create a designated homework station with minimal distractions, proper lighting, and necessary supplies. Studies indicate that a consistent workspace helps children shift into "study mode" more efficiently.
- Break assignments into manageable chunks using the Pomodoro Technique – 25 minutes of focused work followed by a 5-minute break. This approach aligns with children's natural attention spans and cognitive processing abilities.
- Establish a regular homework routine that includes a specific start time and planned breaks. Research demonstrates that consistent schedules help develop executive functioning skills and reduce resistance.
Remember that homework challenges often peak during shifting academic years. If struggles persist despite implementing these strategies, consider consulting your child's teacher or a learning specialist to identify potential underlying issues and develop targeted interventions.
Building Self-Esteem in Children

Beyond academic success, a child's emotional foundation shapes their lifelong confidence and resilience. As a parent, you can actively build your child's self-esteem through consistent, research-backed approaches that create lasting impact.
Incorporate self affirmation practices by encouraging your child to recognize their unique strengths. Have them complete statements like "I'm proud of myself when…" or "I'm getting better at…" These exercises help develop internal validation skills that research shows are critical for long-term emotional wellness.
Implement positive reinforcement strategies by focusing on effort rather than outcomes. When your child attempts something challenging, acknowledge their persistence with specific praise like "You kept trying different ways to solve that puzzle" instead of generic comments like "good job." Studies indicate this approach helps children develop a growth mindset and resilience.
Create opportunities for age-appropriate independence and decision-making. Let your child choose between reasonable options and learn from natural consequences. This builds competence and teaches them to trust their judgment.
Remember to maintain realistic expectations – self-esteem develops gradually through consistent support and authentic experiences.
Teaching Responsibility at Home

Teaching children responsibility at home requires a systematic approach grounded in developmental psychology and behavioral research. By implementing age appropriate chores and daily routines, you'll help your child develop essential life skills while fostering a sense of belonging within the family roles structure.
Research shows that accountability activities and responsibility games create lasting behavioral patterns that serve children throughout their lives.
Your strategy for teaching home responsibilities should follow these evidence-based steps:
- Start with ownership projects that match your child's developmental stage, gradually increasing complexity as they master each level.
- Establish clear teamwork tasks that emphasize the family's interconnected nature, using task rewards strategically to reinforce positive behaviors.
- Implement consequences learning through natural results rather than punishment, allowing children to experience the direct impact of their choices.
When you consistently apply these principles, you'll notice your child developing stronger decision-making skills and greater self-reliance.
Remember that teaching responsibility isn't about perfect execution; it's about creating opportunities for growth through regular practice and gentle guidance. Your patient, structured approach will help build a foundation for lifelong capability and confidence.
Addressing Bullying Issues

Bullying presents one of the most challenging situations parents must navigate in their child's development. Your role in bullying prevention requires a multi-faceted approach that combines empathy development with practical conflict resolution strategies.
You'll need to work closely with your child's school to understand their policies while strengthening your child's self-advocacy skills.
Start by fostering kindness and social skills at home through regular conversations about peer interactions. You'll want to focus on emotional resilience and assertiveness training, teaching your child how to respond confidently to difficult situations.
Don't forget to address cyberbullying education, as digital harassment has become increasingly prevalent.
Parental involvement is essential – maintain open communication strategies with your child and their teachers. Help your child develop bystander intervention skills, encouraging them to support peers who may be experiencing bullying.
If your child's experiencing bullying, document incidents and engage with school administrators. Consider mental health awareness resources if you notice notable changes in their behavior.
Remember that building peer support networks and practicing positive social interactions can greatly reduce bullying vulnerability.
Fostering Independence in Kids

To foster independence in your children, begin by assigning developmentally appropriate tasks that match their capabilities, from simple self-care routines for toddlers to more complex household responsibilities for teens.
Research shows that allowing children to make mistakes and experience natural consequences builds resilience and problem-solving skills, even when it's challenging for parents to resist intervening.
Studies indicate that gradually stepping back while maintaining supportive supervision helps children develop confidence and competence, leading to measurable gains in self-reliance and decision-making abilities.
Age-Appropriate Responsibilities
Every child's journey toward independence begins with age-appropriate responsibilities at home. Research consistently shows that children who participate in household duties develop stronger executive functioning skills and higher self-esteem.
When creating your family's chores checklist, it's crucial to align tasks with age expectations and developmental capabilities.
Consider these evidence-based guidelines for age-appropriate responsibilities:
- Ages 3-5: Simple tasks like putting toys away, helping make their bed, and placing dirty clothes in the hamper develop basic organizational skills and time management.
- Ages 6-9: Feeding pets, helping with laundry sorting, and basic cleaning tasks foster problem-solving abilities and strengthen fine motor skills.
- Ages 10-13: More complex responsibilities like preparing simple meals, cleaning bathrooms, and managing their morning routines build time management and planning abilities.
Studies indicate that children who regularly engage in age-appropriate chores are more likely to become self-sufficient adults.
Remember that consistency matters more than perfection. You'll want to adjust your expectations based on your child's individual development, always ensuring tasks challenge them while remaining achievable.
Let Them Make Mistakes
Making mistakes serves as a vital learning mechanism in child development, with research from developmental psychologists showing that children who are allowed to fail and recover build stronger problem-solving skills and emotional resilience.
You'll need to resist the urge to swoop in and prevent every potential mistake your child might make. Instead, view these moments as learning opportunities for fostering creativity and independent thinking.
When your child faces natural consequences from their decisions, they're developing essential risk assessment and decision-making skills that'll serve them throughout life.
The key is balancing safety with embracing failure. While you shouldn't let your child engage in dangerous activities, you can encourage exploration within reasonable bounds.
When mistakes happen, offer constructive feedback that focuses on the process rather than the outcome. Try saying, "What do you think you could try differently next time?" instead of providing immediate solutions.
Remember that resilience building happens gradually. Your child's ability to bounce back from setbacks strengthens with each experience of overcoming a challenge.
This approach helps develop confident, capable individuals who aren't paralyzed by the fear of making mistakes.
Step Back, Watch Growth
Parents often struggle with finding the right balance between protection and independence, yet research consistently shows that gradually stepping back promotes vital developmental milestones.
By adopting a growth mindset and nurturing patience, you'll create a supportive environment where your child can thrive through natural exploration and discovery.
Research in child development emphasizes three key observation techniques that maximize your child's potential while maintaining appropriate parental involvement:
- Position yourself nearby but resist the urge to intervene immediately – this builds resilience and problem-solving skills
- Provide emotional support through encouraging words and positive reinforcement rather than direct solutions
- Create structured play opportunities that foster curiosity while ensuring safety parameters
You'll notice significant developmental progress when you step back strategically.
Watch as your child develops confidence through independent decision-making and natural consequences.
By maintaining a balanced approach to supervision, you're not just observing growth – you're actively facilitating it.
Remember that your presence as a supportive guardian rather than a constant problem-solver helps your child develop vital life skills while strengthening your parent-child bond.
Effective Discipline Strategies

Through decades of child development research, experts have identified discipline strategies that effectively shape behavior while nurturing a child's emotional well-being.
You'll find that positive reinforcement consistently ranks among the most powerful tools, as it strengthens desired behaviors and builds your child's self-esteem. When you catch your child being good and acknowledge it specifically, you're reinforcing those positive choices.
Natural consequences serve as effective teachers when implemented safely and appropriately. If your child refuses to wear a coat, letting them feel cold (while carrying the coat) teaches more effectively than lectures.
You'll want to establish clear, age-appropriate expectations and maintain consistent responses to misbehavior. When correcting your child, focus on the behavior rather than character traits, using phrases like "that action was unkind" instead of "you're mean."
Remember that discipline means teaching, not punishment. By responding calmly and consistently to misbehavior, you're helping your child develop self-regulation skills.
Create a supportive environment where mistakes are learning opportunities, and you'll foster emotional intelligence alongside behavioral growth.
Bedtime Routine Tips
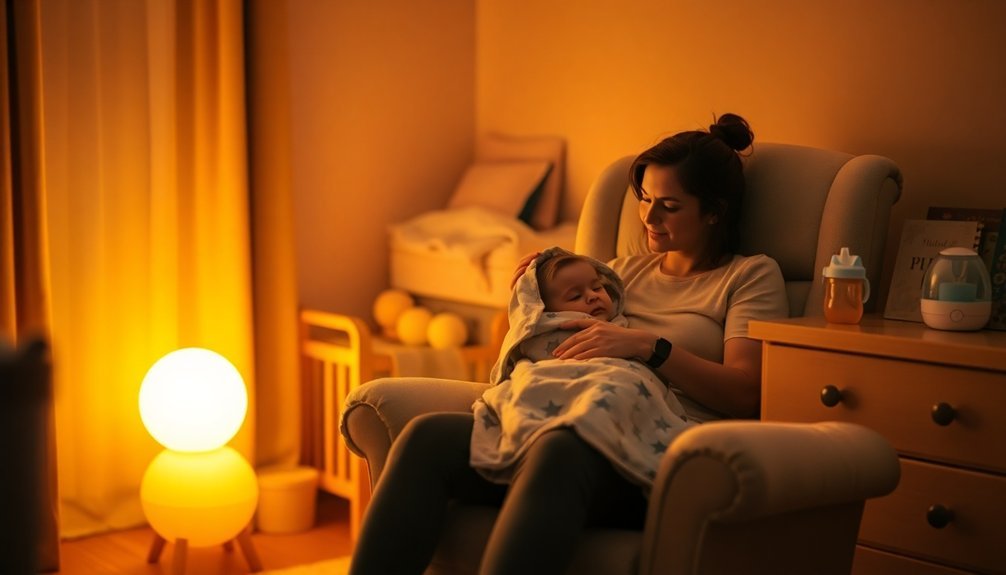

A consistent bedtime routine stands out as one of the most essential factors in children's sleep quality, according to extensive sleep research. When you establish relaxing routines and consistent timing, you'll help your child develop positive sleep associations that can last a lifetime.
Creating a sleep environment that's conducive to rest, incorporating calming activities, and maintaining digital curfews will markedly improve your child's sleep hygiene.
Here's a research-backed sequence for an effective nighttime ritual:
- Start winding down 30-45 minutes before bedtime with quiet activities like bedtime stories, gentle music, or light stretching.
- Offer small bedtime snacks if needed, focusing on foods that combine complex carbohydrates and protein.
- Address nighttime fears through family bonding activities, such as sharing the day's events or practicing simple relaxation techniques.
Remember that sleep training may take time, but your consistent approach to nighttime check-ins will help establish lasting habits.
You'll find that these soothing music and calming activities become cherished moments of connection, transforming bedtime from a potential struggle into a peaceful shift to sleep.
Managing Social Media Use
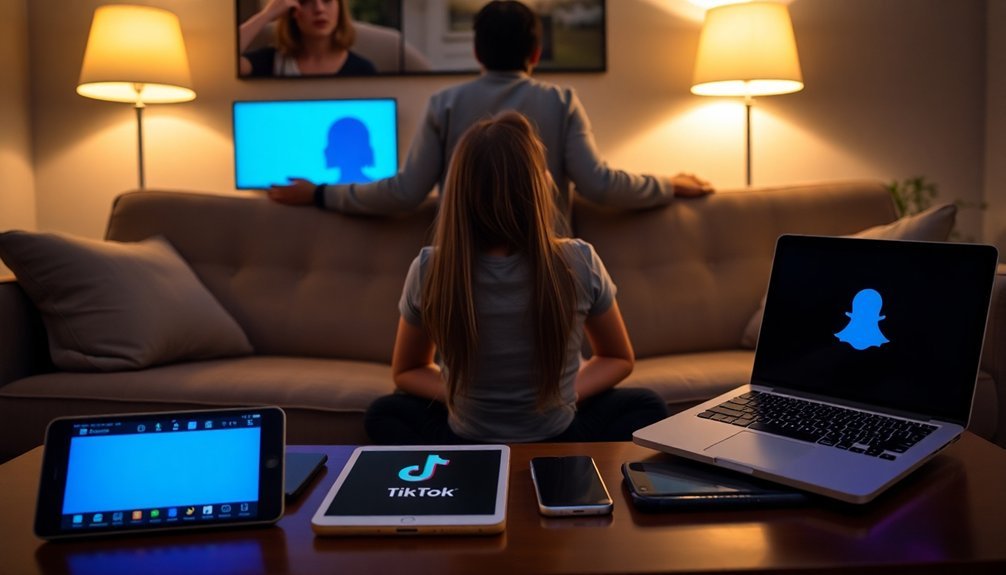

Just as healthy sleep habits protect your child's wellbeing, setting boundaries around social media use safeguards their digital wellness. Research shows that establishing clear social media guidelines and screen time expectations early on helps children develop healthy online habits.
You'll want to focus on online privacy tips, teaching your kids about secure passwords, sharing limits, and digital footprints. Start with age-appropriate platforms and gradually introduce more complex social networks as your child demonstrates responsible behavior.
Digital citizenship education should be ongoing, focusing on fostering online empathy and understanding the impact of their virtual actions. You're not alone in managing distractions online – many parents use apps and tools to help their children stay focused during homework hours.
When monitoring social interactions, strike a balance between supervision and trust. Encourage positive sharing by modeling good behavior and discussing real-world examples of both beneficial and harmful social media use.
Remember to set clear usage boundaries, including device-free meals and daily time limits. Research indicates that children whose parents actively guide their social media use develop stronger digital literacy skills and healthier online relationships.
Teaching Good Hygiene Habits
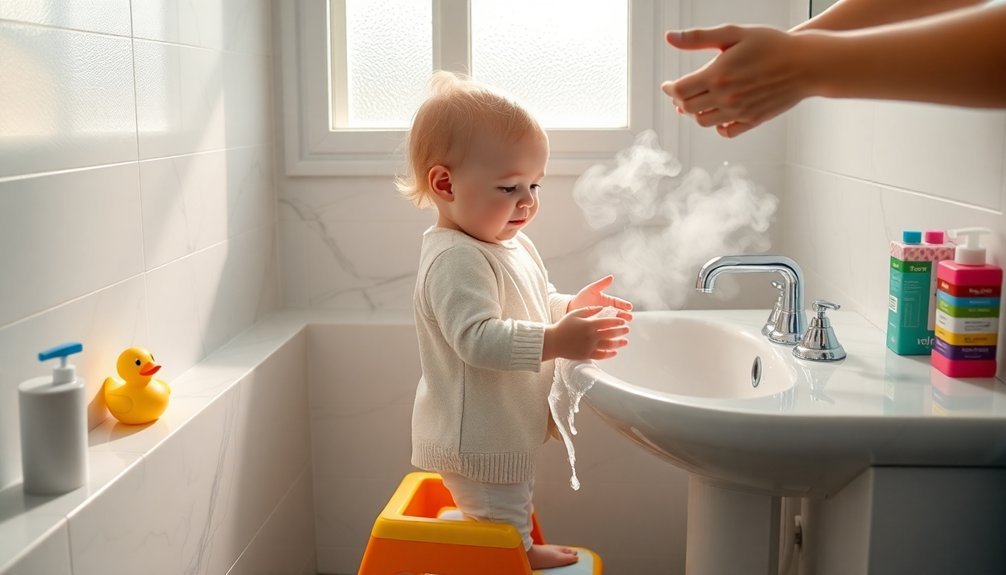

Teaching your children proper hygiene habits requires both creativity and consistency to make these essential practices stick.
You'll find greater success by transforming handwashing into an engaging activity, such as singing favorite songs for timing or using colorful soaps that make the experience more appealing to young minds.
Establishing structured daily routines, backed by research showing that habits form through repetition, helps children internalize important hygiene practices like brushing teeth, bathing, and proper handwashing technique.
Making Handwashing Fun
For many parents, establishing proper handwashing habits can feel like an uphill battle. Research shows that turning hygiene routines into engaging activities greatly increases children's compliance and long-term habit formation.
By incorporating playful elements like handwashing songs and interactive stories, you'll transform this essential health practice into an adventure your kids will enthusiastically anticipate.
Creating a designated splash zone with colorful towels and themed washing supplies makes the experience visually appealing and organized. You can introduce soap science experiments to teach about germ removal while keeping children engaged.
Family challenges and creative contests, supported by reward stickers and sticker charts, provide positive reinforcement that's proven effective in behavioral modification.
Here are three evidence-based strategies to make handwashing irresistible:
- Establish character mascots who demonstrate proper technique through handwashing dances
- Design sensory activities using different soap textures and water temperatures
- Set up fun reminders using musical timers and interactive bathroom decorations
Establishing Daily Cleaning Routines
Beyond handwashing, building thorough hygiene habits requires a structured daily approach that children can follow naturally. Research shows that children thrive on predictable routines, and implementing cleaning charts with reward systems can transform daily hygiene tasks into engaging habits.
| Time of Day | Hygiene Task |
|---|---|
| Morning | Brush teeth, wash face |
| After meals | Clear dishes, wipe mouth |
| After play | Put toys away, clean hands |
| Before bed | Bath/shower, brush teeth |
| As needed | Clean up spills, sanitize |
Create age-appropriate cleaning charts that break down tasks into manageable steps. For children aged 3-5, use picture-based charts; for older kids, incorporate written instructions. Studies indicate that reward systems work best when they're immediate and specific, such as earning stickers for completed tasks or accumulating points toward a desired privilege.
Consistency is key – neuroscience research confirms that it takes approximately 21 days to form a new habit. Track progress using digital apps or traditional charts, and celebrate small victories. Remember to model the behaviors you're teaching, as children learn primarily through observation and imitation of their caregivers' routines.
Encouraging Reading at Home
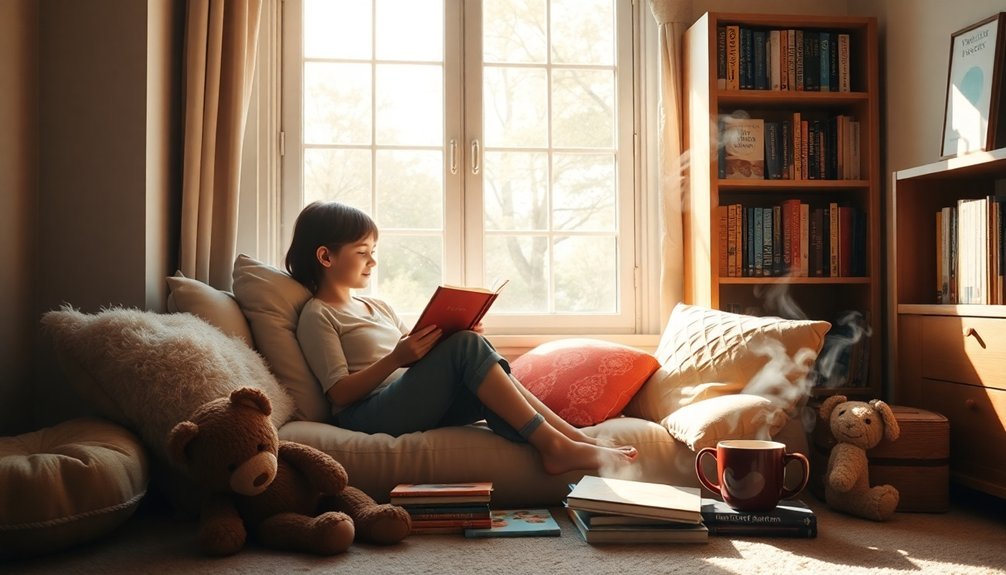

Reading at home builds the foundation for lifelong literacy and academic success. You'll strengthen your child's reading habits by creating consistent reading routines and exploring diverse literature together. Through interactive reading and shared storytelling sessions, you're fostering both comprehension skills and emotional connections with books.
To establish effective reading engagement in your home:
- Set up a dedicated reading space with comfortable seating, good lighting, and easy access to age-appropriate books, incorporating both digital reading options and traditional formats.
- Schedule daily family reading time, combining reading aloud sessions for younger children with quiet reading periods for older ones, and encourage reading partnerships between siblings.
- Create motivational reading challenges with achievable reading goals, using reading logs to track progress and celebrate reading milestones through simple rewards.
Remember to mix up your reading activities with themed reading adventures, genre exploration, and character discussions. Regular library visits keep your book selection fresh, while family book clubs foster deeper reading comprehension through meaningful conversations.
Building Strong Family Bonds
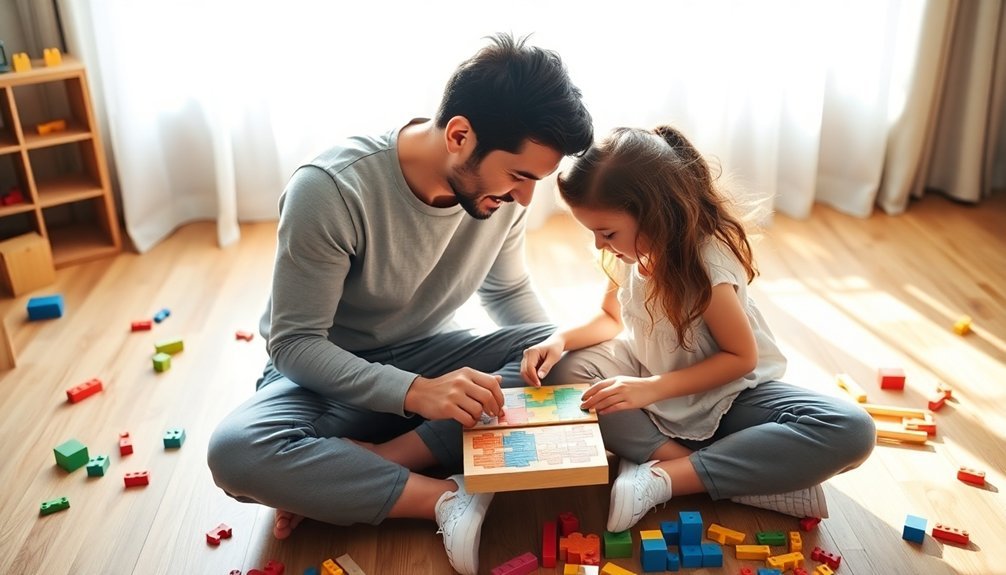

Building meaningful family connections requires consistent, intentional effort and quality time together. Research shows that families who prioritize shared activities and family traditions experience stronger emotional bonding and improved communication patterns. You'll find that establishing regular family rituals, whether daily dinners or weekly game nights, creates predictable opportunities for connection.
Open communication forms the foundation of trust building within families. Create safe spaces for honest dialogue by actively listening without judgment and encouraging everyone to express their feelings. When conflicts arise, use them as opportunities to model effective conflict resolution strategies and reinforce mutual respect.
Engage in teamwork activities that capitalize on each family member's strengths. Whether it's cooking together, working on home projects, or participating in community service, collaborative experiences strengthen family bonds.
Studies indicate that families who spend at least 20 minutes of undivided attention daily on quality time show improved relationship satisfaction and emotional well-being.
Remember to adapt family activities to different ages and interests while maintaining consistency in your commitment to togetherness. This flexibility helps sustain engagement as your children grow and develop.
Dealing With Separation Anxiety

Monitoring your child's reactions to brief separations can help you identify early warning signs of anxiety, such as excessive clinginess, sleep disruption, or physical complaints.
You'll need to implement coping strategies that match your child's developmental stage, from simple games like peek-a-boo for infants to more complex emotional conversations with older children.
Establishing consistent daily routines and predictable goodbye rituals creates a foundation of security and trust, which research shows can greatly reduce separation-related distress in children of all ages.
Recognizing Warning Signs Early
Parents can spot three key warning signs of separation anxiety before it becomes severe. Your child's behaviors often provide clear signals that early intervention may be necessary. By understanding these warning signs, you'll be better equipped to support your child through this challenging developmental phase.
- Your child shows intense distress when anticipating separation, including physical symptoms like stomachaches, headaches, or nausea. Research indicates these manifestations typically appear 20-30 minutes before expected departure times.
- You'll notice your child becoming increasingly clingy or developing new fears about being alone, even in familiar environments. Studies show this behavior often intensifies during change periods like bedtime or school drop-offs.
- Your child demonstrates persistent difficulty sleeping alone or experiences frequent nightmares about separation. According to developmental research, these sleep disruptions can appear weeks before more obvious signs of separation anxiety.
If you observe these patterns consistently for two weeks or longer, it's time to reflect on professional guidance. Early intervention strategies prove most effective when implemented during the initial stages of separation anxiety, with success rates nearly doubling compared to delayed intervention.
Age-Appropriate Coping Strategies
Once warning signs are identified, implementing age-specific coping strategies can markedly reduce separation anxiety symptoms. Research shows that children develop emotional regulation skills at different rates, making it essential to match coping techniques with their developmental stage.
| Age Group | Key Strategies | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Toddlers (1-3) | Comfort objects, peek-a-boo games, predictable routines | Increased security, better changes |
| Preschool (3-5) | Picture schedules, goodbye rituals, mindfulness practices | Improved emotional awareness, reduced clingy behavior |
| School-age (6+) | Self-talk techniques, breathing exercises, journaling | Enhanced independence, stronger self-regulation |
You'll find that introducing age-appropriate strategies gradually helps your child build resilience. For toddlers, start with simple separation games, while preschoolers benefit from visual schedules and basic mindfulness activities like belly breathing. School-age children can learn more complex emotional regulation techniques, including progressive muscle relaxation and positive self-talk. Studies indicate that consistent practice of these strategies leads to significant improvements in 85% of children within 8-12 weeks. Remember to maintain patience during this process, as each child progresses at their own pace.
Building Trust Through Routines
Three key elements of routine-building can greatly reduce separation anxiety in children: consistency, predictability, and gradual changes. When you establish daily structure in your home, you're creating a foundation of emotional security that helps your child navigate changes with greater confidence.
Trust building emerges naturally through these nurturing habits, as your child learns to rely on the safety of familiar patterns.
Research shows that family rituals and bonding activities greatly strengthen parent-child relationships when practiced consistently. To maximize the predictability benefits of routines, implement these evidence-based strategies:
- Create a visual schedule using pictures or simple charts, allowing your child to anticipate and prepare for daily changes.
- Maintain consistent goodbye rituals, such as a special handshake or three hugs, which provide closure and reassurance.
- Practice routine consistency even during weekends and holidays, as this reinforces your child's sense of security.
Through these structured approaches, you'll notice your child developing greater independence and resilience.
Remember that routine adjustments should be introduced gradually, allowing time for adaptation while maintaining the core elements that provide stability and comfort.
Supporting Athletic Development

A child's athletic journey begins long before organized sports, with developmental milestones that build essential movement skills. You'll want to focus on physical literacy through fun activities that develop fundamental movements like running, jumping, and throwing.
Age-appropriate training guarantees your child builds strength and coordination naturally, while preventing injuries that could discourage participation.
Your role in supporting athletic development extends beyond just signing up for teams. You'll need to balance sports with other activities, maintain positive reinforcement, and model sportsmanship values.
When your child shows interest in specific sports, encourage skill development through proper coaching techniques while maintaining peer encouragement and family involvement.
Team dynamics and competitive spirit will emerge naturally as your child progresses. Focus on goal setting and mental toughness development appropriate for their age.
Support their journey with proper sports nutrition and guarantee they're experiencing sports diversity before specializing.
Managing Food Allergies
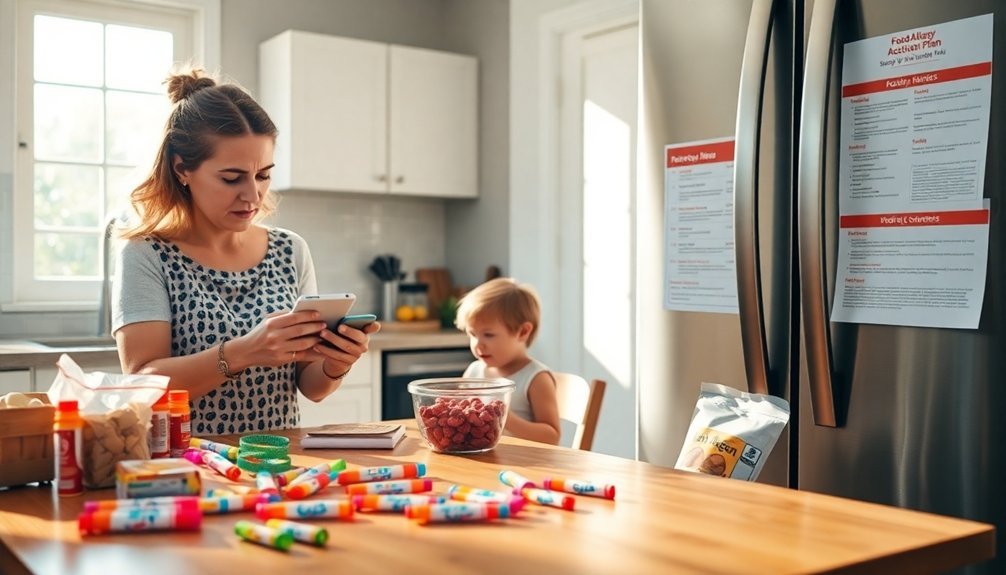

Food allergies in children require vigilant management and clear communication across all caregiving environments. Your child's safety depends on developing thorough food allergy management strategies and ensuring everyone involved in their care understands emergency action plans.
You'll need to master label reading skills and maintain constant cross contamination awareness to create a safe environment.
To effectively manage your child's food allergies, focus on these key areas:
- Build a support system by connecting with school staff, sharing allergy friendly recipes, and joining support group resources where you'll find families facing similar challenges.
- Create detailed allergen avoidance strategies, including safe snack options and family meal planning that accommodates everyone's needs while keeping your allergic child safe.
- Establish clear protocols for different settings, including written emergency action plans, school allergy policies, and communication plans for caregivers.
Remember that successful food allergy management evolves as your child grows.
You'll need to adjust strategies for different developmental stages, from closely supervised toddler years to teaching independent management skills to older children.
Stay informed about the latest research and treatment options through reliable medical sources.
Teaching Internet Safety

Digital safety starts at home with proactive conversations about online risks and responsible Internet use. You'll need to establish clear internet safety tips and social media guidelines that evolve as your child grows.
Start with basic internet etiquette lessons for younger children, then progress to more complex topics like digital footprint management for teens.
Implement screen time protocols that balance online activities with offline engagement. Research shows that children who follow structured safe browsing habits are less likely to encounter inappropriate content or online predators.
You can reinforce online privacy education through regular family discussions and by modeling responsible behavior yourself.
Make cyberbullying awareness a priority by teaching your children to recognize, report, and respond to online harassment.
Set up parental controls understanding that they're tools to support, not replace, active supervision. Regularly review your child's online activities and adjust age-appropriate content filters as needed.
Create a family media agreement that outlines expectations, consequences, and safety protocols. This approach helps children develop critical thinking skills about their digital interactions while maintaining open communication with you about their online experiences.
Balancing Activities and Rest

While managing your child's digital world requires careful attention, establishing a healthy balance between activities and rest forms another cornerstone of effective parenting. Research consistently shows that proper activity balance contributes to improved academic performance, emotional regulation, and physical development.
Studies from the American Academy of Pediatrics emphasize the critical rest importance for growing minds and bodies.
To maintain an ideal equilibrium between engagement and downtime, consider these evidence-based strategies:
- Schedule structured activities for no more than 20 hours per week for school-age children, allowing sufficient free play and relaxation time.
- Maintain consistent sleep schedules, ensuring 9-11 hours of sleep for children aged 6-13, and 8-10 hours for teenagers.
- Include daily "quiet time" periods, even for children who've outgrown naps, promoting mental restoration and stress reduction.
You'll notice improved behavior, concentration, and overall well-being when you implement these balanced routines.
Research indicates that children who maintain regular rest periods alongside enriching activities demonstrate better stress management skills and stronger social connections.
Remember that each child's ideal activity-rest ratio may differ based on their individual temperament and energy levels.
Handling Public Meltdowns

Meltdowns in public spaces present one of parenting's most challenging scenarios, affecting both neurotypical and neurodivergent children. Understanding triggers and implementing proactive planning can greatly reduce their frequency and intensity. You'll need to develop public strategies that work specifically for your child's needs and temperament.
Start by identifying emotional triggers in various settings and establish calming methods before they're needed. You can teach self-regulation skills through role-play at home, building your child's coping mechanisms gradually.
When meltdowns occur, your parent responses should remain consistent and calm, focusing on empathy building rather than punishment. Effective communication strategies include getting down to your child's level, using simple language, and offering choices when possible.
Consider environment adjustments like avoiding crowded times at stores or bringing noise-canceling headphones. Distraction techniques and positive reinforcement can help redirect challenging behaviors before they escalate.
Remember that social awareness from others shouldn't dictate your response – focus on your child's needs while maintaining public patience. Keep a "calm down kit" with familiar comfort items, and practice these techniques regularly to strengthen your child's emotional toolkit.
Discussing Difficult Topics

When approaching challenging conversations about death, loss, sex, or consent with your children, it's crucial to use age-appropriate language and respond to their questions honestly while respecting their emotional readiness.
Research shows that children who receive factual, clear information from trusted adults develop healthier coping mechanisms and understanding of these sensitive topics.
You'll want to maintain an open-door policy for ongoing dialogue, as children process information gradually and may need multiple conversations over time to fully understand these complex subjects.
Death and Loss Conversations
Talking to children about death and loss ranks among the most challenging responsibilities parents face. Research shows that providing age-appropriate explanations and establishing open dialogue helps children process grief more effectively.
You'll need to balance honesty with sensitivity while creating a safe space for emotional expression.
When addressing death with your child, consider these evidence-based approaches:
- Start with clear, concrete language – avoid euphemisms like "passed away" or "gone to sleep," as these can create confusion and anxiety in young minds. Instead, use direct terms while maintaining a gentle tone.
- Implement coping strategies through family rituals and remembrance activities – create memory boxes, plant a garden, or establish annual traditions that honor your loved one's legacy.
- Encourage ongoing grief support through regular check-ins and memory sharing – children often process loss in waves, revisiting their feelings as they reach new developmental stages.
You're not alone in this journey. Professional resources and support groups can guide you through loss education and healing processes.
Remember that every child's grief journey is unique, and there's no perfect timeline for working through these emotions.
Sex and Consent Talks
Parents frequently struggle with initiating age-appropriate conversations about sex and consent, yet research shows that early, open dialogue leads to healthier attitudes and safer decision-making in adolescence. Start by establishing trust building through ongoing conversations about body autonomy from an early age.
| Age Group | Key Topics | Conversation Starters |
|---|---|---|
| 2-5 years | Body parts, private zones, basic boundaries | "Your body belongs to you" |
| 6-12 years | Puberty, personal space, online safety | "Let's talk about changes you might notice" |
| 13+ years | Consent, healthy relationships, sexual safety | "What makes a relationship respectful?" |
Research indicates that children who receive thorough consent education are better equipped to recognize and respecting boundaries in their relationships. When discussing these topics, maintain open dialogue by listening without judgment and empowering choices through accurate information. Use everyday moments as natural teaching opportunities, whether it's discussing a news story or addressing questions about relationships they observe.
Remember that these conversations aren't one-time events but rather age appropriate discussions that evolve as your child develops. Focus on creating a safe space where questions are welcomed and honest answers are provided.
Encouraging Healthy Exercise

Children's physical activity habits are shaped greatly during their early years, making exercise promotion an essential parenting responsibility. Research shows that parents who actively participate in movement routines with their children create lasting fitness habits.
You'll find that incorporating family workouts and outdoor adventures naturally builds exercise motivation while strengthening family bonds.
To effectively encourage healthy exercise, focus on these evidence-based strategies:
- Transform daily activities into playful challenges – turn household chores into dance parties, make backyard cleanup a racing game, or create obstacle courses during regular tasks.
- Schedule regular group activities that prioritize movement – family bike rides, weekend hikes, or neighborhood sports participation can make fitness feel natural and enjoyable.
- Use health education opportunities during active play – discuss how different movements strengthen muscles, improve coordination, and boost energy levels.
Remember that fitness games and varied physical activities help children develop fundamental movement skills.
You don't need structured exercise programs – spontaneous active play throughout the day contributes greatly to their recommended 60 minutes of daily physical activity.
Keep the focus on fun, and you'll nurture a lifelong appreciation for staying active.
Teaching Time Management

While mastering time management skills takes years of practice, early guidance during childhood creates the foundation for lifelong organizational success. Start by introducing basic planning tools and routine establishment techniques that match your child's developmental stage.
| Age Group | Key Skills | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Ages 4-7 | Basic scheduling | Picture charts, timer |
| Ages 8-11 | Priority setting | Weekly planner, checklists |
| Ages 12-14 | Deadline management | Digital calendar, task apps |
| Teens 15+ | Task delegation | Project management tools |
Teaching time blocking helps children break down larger tasks into manageable chunks. You'll want to emphasize schedule flexibility while maintaining core productivity hacks like the Pomodoro technique for focus. Guide them in goal tracking by creating visual progress charts and celebrating small wins.
Remember that different focus techniques work for different children. Some might excel with strict routines, while others need built-in breaks for peak performance. Introduce time management concepts gradually, allowing your child to develop their own system. By incorporating these skills into daily activities, you're helping them build essential habits that will serve them throughout their academic and professional lives.
Developing Social Skills

Your child's social development requires consistent opportunities to practice key interpersonal skills, from making friends at school to resolving conflicts constructively.
Research shows that children who engage in cooperative play and structured social activities demonstrate stronger emotional regulation and higher social competence by elementary school.
You can support your child's social growth by creating playdate opportunities, modeling healthy conflict resolution, and encouraging participation in group activities that build confidence through positive peer interactions.
Making Friends At School
Friendship development plays a significant role in your child's social and emotional growth during the school years. Research shows that children who develop strong friendship skills early on are more likely to maintain healthy relationships throughout their lives.
Through social play and peer interactions, your child learns essential life skills like empathy, cooperation, and conflict resolution.
To support your child in making friends at school, consider these evidence-based strategies:
- Encourage participation in structured activities during recess or after school, as these provide natural opportunities for peer bonding and shared experiences.
- Practice role-playing common social scenarios at home, helping your child develop confidence in initiating conversations and joining group activities.
- Arrange playdates with classmates, which allow for deeper friendship development in a more relaxed setting outside school hours.
Remember that every child develops social connections at their own pace. If your child struggles with making friends, don't hesitate to collaborate with teachers or school counselors.
They can provide valuable insights and create supportive environments that facilitate positive peer interactions and friendship formation.
Handling Conflict With Others
As children navigate their social world, learning to handle conflict constructively becomes a critical developmental milestone. Research shows that children who develop strong conflict resolution skills early on are better equipped to maintain healthy relationships throughout their lives.
You'll need to guide your child through several key strategies. First, teach them to identify and express their emotions appropriately using "I feel" statements. This foundation of effective communication helps prevent misunderstandings and reduces aggressive responses.
Second, encourage active listening by having your child practice repeating back what others say during disagreements. Model problem-solving techniques by breaking conflicts into manageable steps: identify the issue, brainstorm solutions, evaluate options, and choose a path forward together.
Studies indicate that children who learn this systematic approach are more likely to resolve disputes independently. When your child encounters conflict, resist the urge to jump in immediately. Instead, observe whether they're applying learned strategies and only intervene if necessary.
This builds confidence and reinforces their ability to handle disagreements. Remember to praise their efforts at peaceful resolution, as positive reinforcement strengthens these essential social skills.
Building Confidence Through Play
Play serves as a fundamental catalyst for developing children's social confidence and emotional intelligence. Through carefully structured activities and imaginative play, you'll help your child build essential social skills that last a lifetime. Research shows that children who engage in regular playful interactions demonstrate higher levels of self-esteem and better problem-solving abilities.
Role playing scenarios offer powerful opportunities for social development. When you participate in your child's pretend play, you're creating a safe space for them to explore different social situations and emotions. Studies indicate that children who regularly engage in imaginative play show improved empathy and communication skills.
To maximize play-based confidence building:
- Create daily opportunities for unstructured play where your child can take the lead and make decisions.
- Join in role playing scenarios that mirror real-life situations, helping them practice responses to various social challenges.
- Encourage group play dates that allow your child to navigate peer relationships while maintaining their unique identity.
Remember that confidence develops gradually through consistent, positive play experiences. You'll notice your child becoming more socially adept as they practice these skills in a supportive environment.
Managing Gaming Time

Managing your child's gaming time presents one of modern parenting's biggest challenges. Research shows that establishing clear boundaries while maintaining a balanced approach to gaming moderation helps children develop healthy digital habits. Studies indicate that children who follow structured gaming schedules show better academic performance and social development.
You'll want to create a gaming schedule that works for your family's routine. Consider implementing a token system where children earn gaming time through completing homework, chores, or outdoor activities. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends no more than one to two hours of total screen time daily for school-age children.
Transform gaming into a family activity when possible. Family gaming sessions not only help you monitor content but also create opportunities for bonding and skill development. Research from the Digital Games Research Association shows that parents who actively participate in their children's gaming experiences have better insights into setting appropriate limits.
Set up device-free zones and times in your home, particularly during meals and before bedtime. Use parental controls and gaming console settings to automatically limit session lengths, ensuring consistent enforcement of your established boundaries.
Addressing Learning Difficulties

Your child's learning difficulties require early identification and proactive intervention to guarantee ideal developmental outcomes.
Understanding your child's unique learning styles and implementing effective intervention strategies can greatly impact their academic success and emotional well-being. Through parental involvement and teacher collaboration, you'll create a supportive environment that nurtures growth mindset and builds confidence.
To effectively address learning challenges, focus on these key areas:
- Academic support: Partner with teachers to develop specialized programs, explore tutoring options, and provide consistent homework assistance that aligns with your child's learning needs.
- Skill development: Foster self-advocacy skills, enhance social skills, and implement communication techniques that help your child navigate classroom behavior and peer relationships successfully.
- Emotional support: Use positive reinforcement to build resilience, teach coping mechanisms, and celebrate progress to maintain motivation and engagement in learning.
Remember that accessing educational resources early helps prevent learning gaps from widening.
You're not alone in this journey – many parents successfully support their children through learning difficulties by staying informed and maintaining open communication with educational professionals.
Building Emotional Intelligence

Recognizing your child's emotional cues and validating their feelings forms the foundation of emotional intelligence, enabling them to develop self-awareness and empathy.
You'll strengthen your child's emotional vocabulary by naming feelings during daily interactions and modeling appropriate emotional expression.
Teaching problem-solving skills through emotional coaching helps your child identify triggers, consider multiple solutions, and make thoughtful choices when facing challenging situations.
Understanding Your Child's Feelings
Emotional intelligence begins to develop during early childhood, laying the foundation for lifelong social and emotional competence. Your child's ability to understand and express feelings shapes their emotional regulation skills and empathy development. By actively engaging in emotional validation and helping them build a feelings vocabulary, you're strengthening their capacity for healthy emotional expression.
When your child experiences complex emotions like sadness or anxiety, understanding their triggers becomes essential. You'll notice that children process emotions differently at various developmental stages. Recognizing these patterns helps you provide appropriate support while building resilience.
Here are three evidence-based strategies for nurturing your child's emotional awareness:
- Create a safe space for expressing joy, sadness, and all emotions in between by modeling authentic emotional expression yourself.
- Practice active listening without immediately trying to fix their feelings, allowing them to fully process their emotional experiences.
- Use daily situations as opportunities to discuss emotions, helping them connect feelings to specific events and develop problem-solving skills.
Stay consistent with these approaches, as emotional intelligence develops gradually through repeated experiences and supportive guidance.
Teaching Emotional Problem-Solving
Problem-solving skills form the backbone of emotional intelligence, enabling children to navigate challenging situations with growing confidence and competence. When you teach your child emotional problem-solving, you're building their capacity for emotional awareness and frustration tolerance through real-world practice.
Start by modeling active listening and perspective taking during family conflicts. You'll strengthen your child's empathy development by asking questions like "How do you think your friend felt?" or "What might solve this problem for both of you?"
Guide them through problem identification by breaking down complex situations into manageable parts. Encourage solution brainstorming by helping your child generate multiple options for handling difficult emotions. You can say, "Let's think of three different ways to handle this."
Practice emotional regulation techniques together, such as deep breathing or counting to ten. When your child uses effective coping strategies, acknowledge their growth with specific praise.
Remember that conflict resolution skills develop gradually. Your consistent support in teaching these tools will help your child build a strong foundation for lifelong emotional problem-solving abilities.
Teaching Safety Rules

Teaching children about safety rules consistently ranks among parents' top priorities, as research shows that early safety education greatly reduces the risk of preventable accidents and injuries.
You'll find that children learn safety best through consistent repetition, hands-on practice, and age-appropriate explanations. Research indicates that starting with basic concepts like fire safety and stranger danger around age three, then gradually introducing more complex topics like internet rules and first aid, yields the best results.
To effectively teach safety rules, focus on these evidence-based strategies:
- Model safe behaviors yourself, whether it's practicing kitchen safety or demonstrating proper road safety techniques.
- Create regular safety drills that address home hazards and emergency situations, ensuring your child knows emergency contacts.
- Use role-playing scenarios to teach concepts like safe playground behavior and stranger awareness.
Studies show that children who understand the "why" behind safety rules are more likely to follow them consistently.
When discussing safety measures, maintain a calm, matter-of-fact tone to avoid creating anxiety while still conveying the importance of these life-protecting behaviors.
Managing Technology Use

While establishing safety rules helps protect children in the physical world, today's parents must also navigate the complex landscape of digital safety and screen time.
Research shows that setting clear boundaries around technology balance is essential for healthy development, including implementing tech free zones and device free meals to maintain family connections.
Start by understanding age restrictions for various platforms and establishing parental controls on all devices.
Focus on building digital literacy skills while teaching online etiquette and cyberbullying awareness.
Monitor your child's online relationships and tech communication patterns, paying special attention to social media impact on their well-being.
Balance is key – recognize both gaming benefits and the importance of gaming moderation.
Choose educational apps carefully, using trusted app recommendations to support virtual learning.
Create a family technology plan that addresses internet privacy, screen time limits, and tech monitoring strategies.
Watch for signs of tech addiction, such as withdrawal from physical activities or declining academic performance.
Remember that you're modeling healthy tech habits – children often mirror their parents' behavior.
Regular family discussions about technology use help maintain open communication and trust.
Encouraging Creative Expression

Creative expression helps children develop critical thinking skills and emotional intelligence, according to extensive child development research. When you create opportunities for artistic exploration and hands-on projects, you're nurturing your child's cognitive development and self-expression abilities.
To effectively encourage your child's creativity while maintaining structure, consider these research-backed approaches:
- Rotate creative activities daily: Alternate between expressive dance, musical improvisation, and creative storytelling to engage different parts of your child's brain and maintain enthusiasm.
- Set up dedicated creativity zones: Create spaces for role-playing activities, puppet making, and building with blocks, ensuring materials are accessible and organized for spontaneous creative moments.
- Integrate creativity into daily routines: Transform ordinary activities into creative opportunities through themed dress-up during chores, nature-inspired art during outdoor time, and creative cooking during meal prep.
Research shows that children who engage in regular collaborative projects and sensory art experiences demonstrate enhanced problem-solving abilities and social skills.
You'll strengthen your parent-child bond while fostering innovation through DIY science experiments, photography challenges, and community art projects.
Building Problem-Solving Skills

When you consistently allow your child to work through real-world challenges, like organizing their school supplies or planning a playdate, you help them develop essential problem-solving abilities.
Research shows that children learn best from hands-on experiences where they can test solutions and experience natural consequences in a supported environment.
Teaching Through Real Situations
Real-life situations provide the most effective opportunities for children to develop essential problem-solving abilities. When you engage your child in experiential learning through everyday examples, you're creating powerful teaching moments that stick.
Research shows that contextual understanding through hands-on experiences leads to better retention and practical application of life skills.
You'll find that situational teaching works best when you follow these key strategies:
- Notice natural opportunities for problem-solving scenarios throughout the day, such as sharing toys, managing time, or handling conflicts with siblings.
- Guide your child through interactive storytelling about their experiences, helping them identify different solutions and potential outcomes.
- Allow them to experience natural consequences in safe situations, which builds their confidence in making decisions.
Fostering Independent Decision Making
Building on the foundation of real-world learning experiences, parents can actively foster their child's independent decision-making abilities through structured yet flexible guidance.
You'll need to create problem-solving opportunities that allow your child to practice critical thinking while maintaining appropriate freedom limits for their age and development.
Start by offering simple choices in daily activities, gradually increasing complexity as your child demonstrates readiness.
When they're facing challenges, resist the urge to provide immediate solutions. Instead, guide them through self-directed learning by asking open-ended questions that encourage risk assessment and thoughtful analysis.
Create a supportive environment where your child feels safe making independent choices and experiencing their consequences.
Remember that mistakes are valuable learning opportunities. When your child makes a poor decision, help them analyze what went wrong and brainstorm better alternatives for the future.
Focus on confidence building by acknowledging their decision-making process rather than just the outcome.
As they demonstrate responsible choices, expand their guided independence.
This measured approach helps develop lifelong problem-solving skills while ensuring they feel supported throughout their journey toward autonomous decision-making.
Teaching Financial Responsibility

Through early financial education, children develop essential money management skills that shape their future economic well-being. Research shows that children who learn financial literacy before age 12 are more likely to demonstrate strong money management abilities as adults.
You'll empower your children's financial independence by introducing budgeting basics and saving habits early.
Start with these evidence-based strategies to build your child's economic awareness:
- Implement allowance strategies tied to specific tasks, helping children understand the connection between earning potential and effort while teaching expense tracking.
- Create age-appropriate savings challenges and financial goals, incorporating both short-term and long-term wealth building objectives that reinforce delayed gratification.
- Guide regular money conversations about spending choices, charitable giving, and basic investment concepts, ensuring your children develop a well-rounded understanding of financial responsibility.
Remember to adjust your parental guidance based on your child's developmental stage.
Introduce debt awareness and credit understanding gradually, focusing first on fundamental concepts like saving and budgeting. By consistently modeling responsible financial behavior and engaging in open discussions about money, you'll help your children develop vital skills for their financial future.
Developing Healthy Eating Habits

Children's eating patterns established during their formative years greatly influence their lifelong relationship with food. You'll set your kids up for success by implementing meal planning strategies and involving them in grocery shopping decisions. When they participate in selecting fresh ingredients and cooking together, they're more likely to try new foods and develop an interest in nutrition.
Make family meals a priority, as they create opportunities for food exploration and meaningful conversations about healthy choices. You'll find that practicing portion control becomes natural when you demonstrate mindful eating habits. Don't force clean plates; instead, teach your children to listen to their hunger cues.
Focus on nutrition education through hands-on experiences, like planting a small herb garden or reading food labels together. You'll want to offer a variety of nutritious foods without labeling them as "good" or "bad." Use positive reinforcement when your children try new foods, but avoid using treats as rewards.
Create a supportive environment where meals are enjoyable, not stressful, and remember that your own eating behaviors markedly impact your children's relationship with food.
Managing School Stress
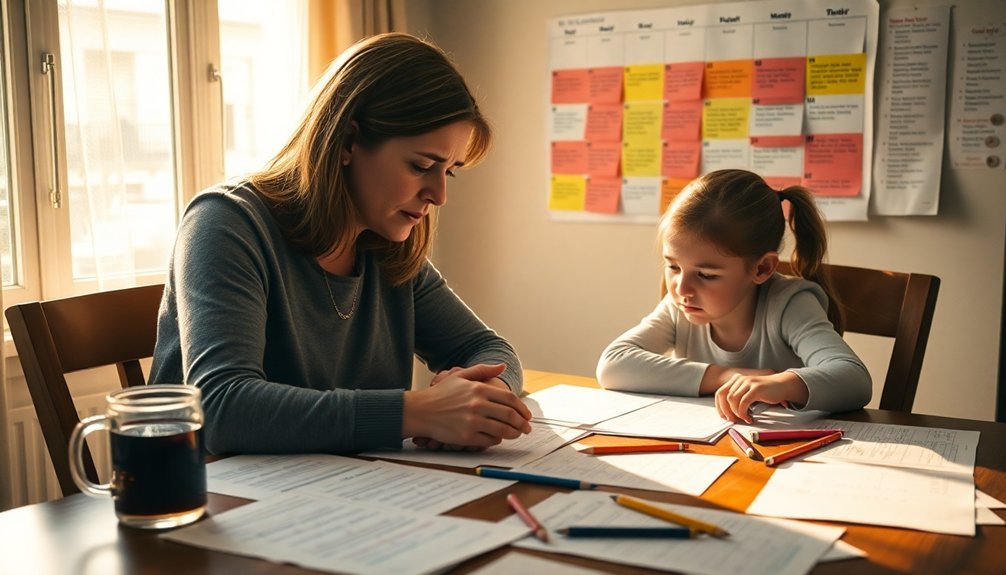

Students frequently encounter academic pressure that can affect their mental well-being and performance. As a parent, you'll want to help your child develop effective stress management techniques and coping mechanisms that promote resilience. Research shows that implementing consistent emotional support strategies can greatly reduce academic anxiety and improve learning outcomes.
You can help your child manage school-related stress through these evidence-based approaches:
- Establish structured time management skills by breaking homework into manageable chunks, using a planner, and creating realistic study schedules that include regular breaks for relaxation activities.
- Incorporate mindfulness practices like deep breathing exercises, stress reduction games, or quiet reading time before bedtime to help your child decompress and process the day's challenges.
- Apply positive reinforcement methods by celebrating effort rather than grades, acknowledging progress, and maintaining open communication about academic pressure relief strategies.
Remember that each child responds differently to academic pressure, so it's vital to customize anxiety management tips based on your child's unique needs.
Monitor their stress levels regularly and adjust support strategies accordingly to maintain a healthy balance between achievement and well-being.
Teaching Personal Boundaries

Teaching your children about personal boundaries starts with establishing clear family rules about privacy, consent, and respectful behavior.
You'll need to consistently model and reinforce these boundaries by acknowledging your children's right to say "no" in appropriate situations and respecting their personal space.
Research shows that children who understand and can maintain healthy boundaries are better equipped to navigate social relationships and protect themselves from potential abuse.
Setting Clear Family Rules
Through consistent boundary-setting, families establish the foundation for healthy relationships and emotional well-being.
When you engage in collaborative decision making through regular family meetings, you're creating a framework for clear behavioral expectations that everyone understands and supports.
Family communication becomes stronger when rule flexibility meets rule consistency, allowing for natural growth while maintaining structure.
To establish effective family agreements, focus on these essential components:
- Expectation clarity: Define rules in specific, measurable terms that all family members can understand and follow, ensuring there's no room for misinterpretation.
- Consequence understanding: Discuss and agree upon logical outcomes for both following and breaking rules, emphasizing positive reinforcement over punishment.
- Regular review and adjustment: Schedule monthly family meetings to evaluate rules' effectiveness and make necessary modifications as your children grow and family dynamics evolve.
Remember that successful family rules aren't about rigid control but rather creating a supportive framework where everyone thrives.
Respecting Others' Space
Personal boundaries serve as essential building blocks for healthy relationships and emotional development in children. Teaching your kids about personal space and boundary setting early on helps them develop vital social awareness and respect for others.
Start by modeling respectful interactions in your home. When your child needs privacy, honor their request, and explain why it's important to respect emotional distance. You'll help them understand that everyone deserves their own space, whether physical or emotional.
Introduce consent education through daily activities. Teach them to ask before hugging friends, borrowing items, or entering someone's room. This builds their understanding of physical boundaries and spatial awareness in shared environments.
Create clear rules about knocking before entering rooms and respecting closed doors. These practical lessons help children internalize privacy respect. Research shows that children who understand personal boundaries are more likely to develop healthy relationships and better self-advocacy skills.
Remember to adjust your teaching approach based on your child's age and developmental stage. Younger children might need more concrete examples, while older kids can grasp more complex concepts about personal space and boundaries.
Teaching "No" Means No
Establishing a firm understanding of the word "no" builds directly upon spatial awareness and boundary lessons. Teaching respect through consistent enforcement helps children develop strong assertiveness training skills while understanding consequences of their actions.
When you model behavior that demonstrates respectful communication, your child learns essential crisis management tools for maneuvering social interactions.
Teaching "no means no" requires a systematic approach to reinforcing boundaries:
- Respond immediately when your child says "no" to unwanted touch or interaction, supporting their right to set limits and validating their emotional responses.
- Practice role-playing scenarios where your child can safely express boundaries, helping them develop confidence in their assertiveness skills.
- Demonstrate proper responses when someone tells you "no," showing how to handle rejection respectfully and without argument.
Remember that setting limits isn't about punishment – it's about teaching respect through consistent, clear expectations.
When children understand their right to say "no" and have that boundary honored, they're more likely to respect others' boundaries in return. This foundational skill supports healthy relationships and emotional development throughout their lives.
Supporting Mental Health

Mental health forms the foundation of a child's overall wellbeing and future success. As a parent, you'll need to actively support your child's emotional development by creating a safe space for expressing feelings and accessing mental health resources when needed.
| Warning Signs | Supportive Actions |
|---|---|
| Social withdrawal | Schedule quality time daily |
| Sleep changes | Maintain consistent routines |
| Mood swings | Listen without judgment |
| Academic decline | Seek professional help |
| Behavioral changes | Build coping skills |
Research shows that children whose parents provide consistent emotional support are better equipped to handle life's challenges. You can strengthen your child's mental health by implementing daily check-ins, practicing mindfulness together, and modeling healthy emotional expression. If you notice concerning changes in behavior, don't hesitate to consult mental health professionals.
Create a home environment where mental health conversations are normalized and feelings are validated. Remember that supporting your child's mental health isn't just about addressing problems – it's about building resilience, self-awareness, and emotional intelligence that will serve them throughout their lives. Stay connected with your child's teachers and healthcare providers to guarantee thorough support across all environments.
Building Academic Success

Establishing strong academic foundations begins with your proactive involvement in your child's early learning routines and study habits.
You'll strengthen your child's educational journey by creating structured homework times, maintaining a dedicated study space, and modeling a positive attitude toward learning.
Research shows that consistent communication with teachers and active participation in school activities greatly boost your child's academic performance and motivation to learn.
Fostering Study Habits Early
Strong study habits planted during a child's early years can bloom into lifelong academic success. By introducing effective study techniques early, you'll help your child develop the foundation needed for future academic challenges. Research shows that early motivation and positive learning experiences greatly impact long-term educational outcomes.
Creating an environment that nurtures learning begins with consistent routines and clear expectations. You'll want to establish a dedicated study space where your child can focus without distractions. Studies indicate that children who develop structured study habits before age eight are more likely to maintain them throughout their academic career.
Consider these research-backed strategies to foster effective study habits:
- Set specific study times each day, even if it's just 15 minutes for younger children.
- Break tasks into manageable chunks and use visual timers to help maintain focus.
- Incorporate multi-sensory learning approaches that align with your child's learning style.
Supporting School-Home Partnership
Three key factors drive successful academic outcomes: consistent communication, active involvement, and aligned expectations between parents and teachers.
To strengthen school communication, establish regular check-ins with your child's teacher through email, apps, or scheduled conferences. You'll stay informed about classroom progress while creating valuable feedback loops that benefit your child's learning journey.
Parent involvement extends beyond homework help. Participate in school events, volunteer when possible, and engage with educational resources provided by teachers.
When you're actively present in your child's learning environments, you'll better understand the support frameworks needed at home to reinforce classroom concepts.
Teacher collaboration works best when you maintain consistent messaging between home and school. Share insights about your child's learning style, challenges, and interests.
This family engagement helps teachers tailor their approach while enabling you to extend classroom strategies at home. Create a shared vision for your child's success by discussing academic goals, behavioral expectations, and potential areas for growth.
Teaching About Body Safety

Teaching children about body safety remains one of the most essential responsibilities parents face in today's world. Through consistent consent education and trust building, you'll help your child develop body confidence and understand personal space boundaries.
It's vital to start these conversations early, using age-appropriate language that empowers your child to recognize and respond to potentially harmful situations.
Consider these evidence-based strategies for teaching body safety:
- Establish clear vocabulary for private areas and consistently reinforce that these parts are personal, helping your child understand their right to body autonomy.
- Practice reading and expressing body language through role-play scenarios, teaching your child to recognize both safe touch and uncomfortable situations.
- Create regular opportunities for open dialogue about empowerment strategies, ensuring your child knows they can always come to you with concerns or questions.
Remember that these conversations shouldn't be one-time events. Research shows that children who receive ongoing body safety education are better equipped to recognize inappropriate behavior and more likely to report concerns to trusted adults.
Managing Peer Pressure
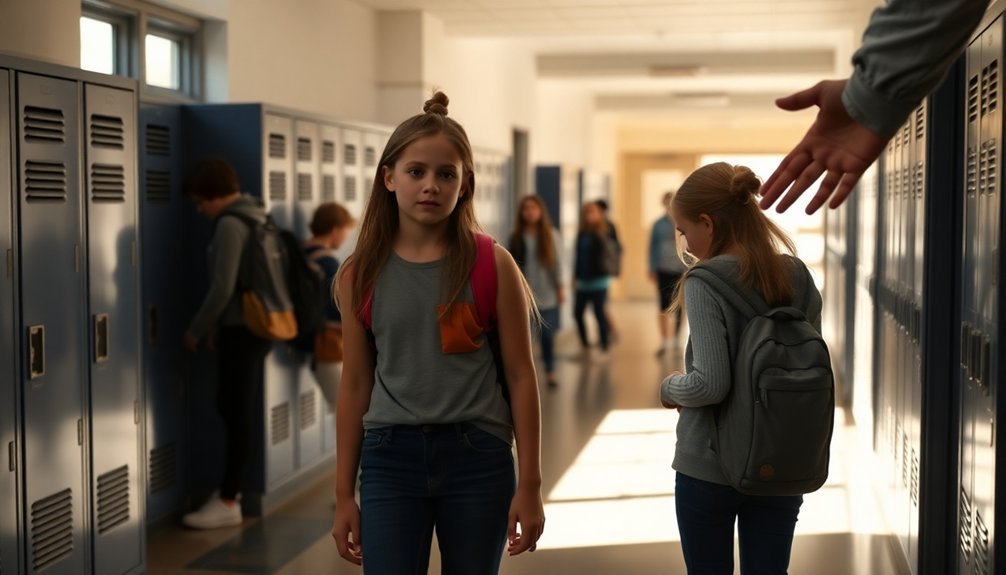
Peer pressure represents one of the most significant social challenges children face throughout their developmental years. When you equip your child with effective peer influence strategies, you'll help them navigate complex social situations while maintaining their values and self-esteem.
Start by fostering open communication at home, creating a safe space where your child can discuss social challenges without fear of judgment. Research shows that children who regularly communicate with parents about peer situations are better at resisting negative behaviors.
Role-play different scenarios to help your child practice saying "no" confidently.
Strengthen your child's self-confidence by acknowledging their positive choices and encouraging independent thinking. Studies indicate that children with higher self-esteem are less likely to succumb to harmful peer pressure.
Teach them to recognize the difference between positive peer influence (like joining study groups) and negative pressure (such as engaging in risky behaviors).
Connect your child with positive peer groups through structured activities and help them develop strong friendships with peers who share similar values.
Remember to monitor their social circles while respecting their growing need for independence and social development.
Encouraging Environmental Awareness

Just as children learn to navigate social influences, they can develop a meaningful connection to the natural world around them. Fostering environmental stewardship starts with simple eco-friendly habits that you can model at home.
Research shows that children who develop conservation awareness early are more likely to maintain sustainable practices throughout their lives.
You'll find success in building environmental consciousness through these proven approaches:
- Make nature exploration a regular family activity – whether it's hiking local trails, bird watching, or maintaining a small garden, these experiences create lasting connections to wildlife protection.
- Integrate recycling education naturally into daily routines – help your child understand how sorting materials and reducing waste contributes to planet protection.
- Engage in age-appropriate climate change discussions that emphasize hope and action – focus on green initiatives your family can implement together.
Remember that children learn best through hands-on experiences.
When you participate in local environmental programs or start home-based conservation projects, you're not just teaching sustainable practices – you're cultivating a generation of informed environmental advocates who understand their role in protecting our planet's future.
Fostering Cultural Understanding

Raising culturally aware children has become increasingly essential in our interconnected world. You'll find that fostering cultural understanding through diverse celebrations and global perspectives helps your children develop empathy and respect for others. Research shows that children exposed to multicultural education before age eight demonstrate stronger social skills and adaptability.
Start by incorporating world cuisines and cultural traditions into your family routines. You can engage in storytelling practices that highlight different heritage exploration experiences, and participate in cultural festivals within your community.
Encourage cross-cultural friendships and language learning opportunities, which studies indicate boost cognitive development and social awareness. Create opportunities for identity exploration through art appreciation and inclusive language at home.
You'll want to discuss historical context age-appropriately, touching on social justice topics when your children are ready. Consider involving your family in community events that celebrate religious awareness and diverse traditions.
Research indicates that children who understand their family heritage while exploring other cultures develop stronger self-identity and cultural competence. Through travel experiences or virtual cultural exchanges, you can help your children build meaningful connections across cultural boundaries.
Building Resilience in Children

While many parents focus on protecting their children from hardship, research shows that controlled exposure to challenges actually strengthens emotional development. Building emotional resilience in children requires a delicate balance between support and allowing them to navigate age-appropriate difficulties.
Studies consistently demonstrate that children who develop positive coping skills early in life are better equipped to handle future challenges.
To foster resilience in your child's daily life:
- Let them experience natural consequences of their actions when safe to do so – this builds problem-solving skills and accountability.
- Validate their emotions while avoiding the urge to immediately fix their problems – this develops emotional regulation and independence.
- Help them reframe setbacks as learning opportunities – this cultivates a growth mindset and adaptability.
Research from child development experts indicates that resilient children share common traits: they're more likely to take healthy risks, bounce back from disappointments, and maintain optimistic outlooks.
You'll notice your child developing greater confidence as they successfully navigate challenges. Remember that building resilience is a gradual process that requires consistency and patience from parents.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can I Effectively Co-Parent After Divorce?
Successful co-parenting starts with clear communication strategies and a detailed parenting plan.
You'll want to keep conversations focused on the children, using business-like communication when needed.
Establish consistent routines between homes, share important information promptly, and never use your kids as messengers.
Research shows children adjust better when parents maintain respectful interactions and follow agreed-upon schedules.
Consider using co-parenting apps to help coordinate and document arrangements effectively.
When Should I Let My Child Wear Makeup?
There's no universal "right age" for makeup, but you'll want to reflect on your child's maturity and your family's values when setting makeup guidelines.
Many experts suggest starting with tinted lip balm or clear mascara around age 12-13, gradually introducing more products as teens develop.
Focus on age-appropriate choices, skin health, and proper application techniques.
How Do I Explain Death and Grief to My Young Child?
Just as seasons change and flowers fade, you'll need to help your child understand life's natural cycles. When explaining death, use clear, age-appropriate language and avoid confusing metaphors like "sleeping" or "gone away."
Research shows children process death concepts differently at various developmental stages. You can validate their grief expressions through art, play, or storytelling.
Should I Let My Child Quit Musical Instruments They Started Learning?
While it's important to teach commitment, forcing your child to continue with an instrument they strongly dislike can backfire.
Research shows that allowing controlled choice in activities supports healthy passion exploration and motivation.
Consider setting a minimum time commitment (like finishing the semester) before letting them quit, and discuss their reasons.
This balanced approach helps your child learn perseverance while respecting their developing interests and autonomy.
How Do I Handle My Child's First Crush or Romantic Interest?
You might be tempted to build a fortress around your child or pretend those butterflies don't exist, but let's get real.
Your child's first crush is a normal developmental milestone that deserves your gentle guidance. Start by creating an open dialogue where they feel safe discussing feelings.
Set clear relationship boundaries while validating their emotions. Research shows that children whose parents approach these conversations supportively develop healthier attitudes toward relationships later in life.
Conclusion
Parenting challenges flow like river rapids – constantly changing yet navigable with the right tools. You've now got research-backed answers to the most pressing questions about raising children, from sleep training to cultural awareness. By implementing these evidence-based strategies, you'll build a strong foundation for your child's development. Remember, while every child's journey is unique, these proven approaches will help you navigate the complexities of modern parenting with confidence.








0 responses to “Top 50 Parenting Questions Answered”
While best first foods for babies is insightful, I wonder if these foods are universally suitable? Cultural differences can play a part, cant they?
Interesting read, but arent toddler tantrums rather subjective? What works for one child may not for another. Thoughts?
Interesting read, but wouldnt it be helpful to include some advice on navigating the teenage years too?